
For a country, that could mean GDP divided by the total number of hours worked by all workers. Few people understand it and even more people dismiss it because they are pretty sure crude oil grows on trees, like goats appear to grow on trees, and America will NEVER run out of oil. Another factor that the ratio fails to account for is the continually increasing demand for natural resources as the global population grows and new economic powerhouses emerge.
Products
For example, suppose the real GDP of an economy is $10 trillion and the aggregate hours of labor in the country is 300 billion. The labor productivity would be $10 trillion divided by 300 billion, equaling about $33 per labor hour. If the real GDP of the same economy grows to $20 trillion the next year and its labor hours increase to 350 billion, the economy’s growth in labor productivity would be 72 percent.
ways employees can trick your monitoring software
In this post, we will explore the basic methods of approximating production capacity from the actual output and calculating single and multiple-item production capacities using machine hours and throughput time. We also look at how production planning software can largely automate this process and enable accurate, data-based capacity fifo vs lifo inventory valuation planning. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, labor productivity (or employee productivity) is the ratio of the goods and services produced (output) to the labor hours (input) required for the production process. While this is a reliable way of estimating actual output, it doesn’t accurately depict production capacity.
- You can filter the industries by sector in the chart below to see a breakdown of the top industries with the highest Current ratio for every sector.
- One example is PVWatts, which was developed by National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
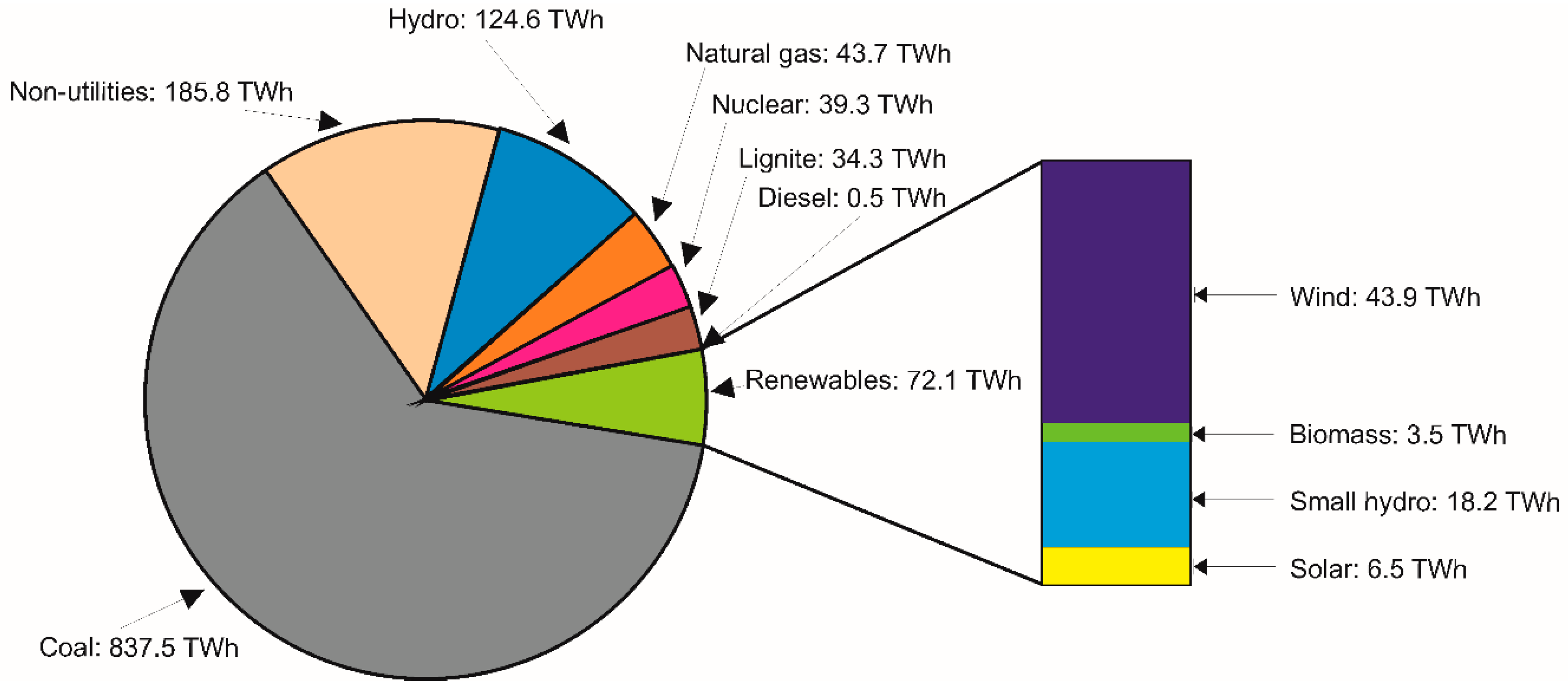
- The United States usually produces an average of over 11 million barrels per day of crude oil.
- If Botswana was seen as having a low reserves-to-production ratio for its diamond industry, it would mean that the nation is running short on one of the natural resources that contribute most to its national economy.
What is the employee productivity ratio?
Whereas manual calculation might suffice to clarify short-term plans, this type of software also makes accurate long-term capacity planning possible. The capacity utilization rate is calculated by dividing the actual capacity by the production capacity and multiplying the result by 100 to obtain a percentage. Manufacturing costs to total expenses is a financial metric that measures this proportion. A higher calculated result indicates more expenses are attributable to costs directly needed to manufacture the product.
The importance of Key Performance Indicators in manufacturing
The real 2009 EP of the 2-axis flat plate systems is 56% higher than that of the CPV (see Table 17). The PR value is 77.5% for 2-axis flat plate and 61.1% for CPV (see Table 17). Where Wtorch is the plasma torch power (MW), ηtorch is the thermal efficiency of the plasma torch, ηelectric is the electrical efficiency of the plasma torch. Where CCE is carbon conversion efficiency (%), Ydrygas is a dry gas yield in Nm3 per kg of dry feedstock (Nm3/kg), CO, CO2, CH4, C2H2, C2H4 and C2H6 are in % (v/v), and C is in % of carbon in the dry feedstock. As can be seen in Table 4.20, recovery alone cannot be an evidence of declining reserve because the recovery to reserve ratio varies largely among different countries.
The reserves-to-production ratio is used to estimate the productive life of a particular site, such as an oil field. Alternatively, it may be used to project national or global availability of a natural resource. Table 4.23 shows total oil reserve as well as reserve/production ratio of top oil producing countries. One example is PVWatts, developed by National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). Capacity utilization measures how much a line, plant, or factory uses its total production capacity. For example, if you have the potential to significantly expand orders, you should check your capacity utilization before agreeing to deliver the product.
The manufacturing industry is no different, having its own special characteristics. Utilizing the ratios above should help you better understand manufacturing companies. Profitability ratios are financial metrics used to assess the profitability of a company. Common profitability ratios include gross profit, operating profit, net profit, EBITDA, return on assets, and return on equity.
This will help you understand whether you could fulfill an expansion with existing capacity, or if you need to adjust your production. A basic way to find out the production capacity is by multiplying the number of available workstation capacity by the available time in a work shift. For example, if a machine’s design capacity is 10 units in an hour and the work shift is 8 hours, the production capacity for the machine is 80 units per shift. A credible alternative to the above is increasing production capacity by using existing resources. This is a plausible approach for almost any manufacturing company, save for ones that are already operating at peak performance.
Companies often strive for high production rates to help lower the time and cost of a project or the production process. However, a higher production rate can also lead to a decrease in quality if more mistakes are made as employees push to have more units produced or more of a building completed. As a result, there is a point in the process at which a decrease in quality can lead to higher costs, even as the production or construction process is taking less time. Labor productivity is closely related to GDP, but they are not the same. On the other hand, labor productivity measures output per unit of labor.
The easiest method is to measure the actual output of units for past time periods and corroborate an average production capacity based on that. A more advanced method is to calculate the machine-hour capacity of the plant and divide it by the throughput time of a product. The most precise way, however, is by adopting capacity planning software which takes into account manufacturing constraints and routings and calculates capacity based on real-world manufacturing data.








